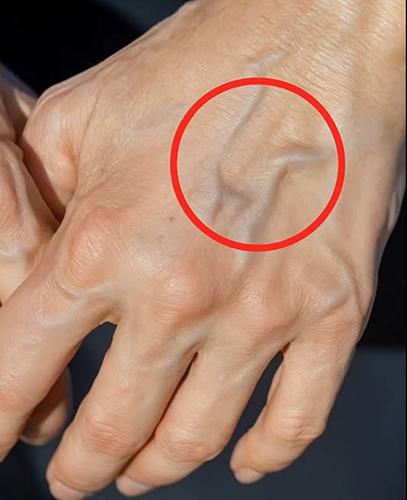
Bulging or visible veins are a common physical occurrence that many people notice, especially on their arms or legs. In most cases, these bulging veins are harmless and related to temporary or natural body changes. However, there are times when they may indicate an underlying medical issue that shouldn’t be ignored. Veins can appear more prominent due to several everyday factors. These include intense physical activity (which increases blood flow and pressure), hot weather (which causes veins to dilate), and aging, which naturally leads to thinner skin and weakened vein walls, making veins easier to see.
Genetics also plays a role; some people are more predisposed to visible veins due to inherited vein structure or skin tone. Additionally, tight clothing, excess body weight, or low body fat can all make veins appear more pronounced, especially in the limbs. However, when veins begin to bulge significantly, become discolored, or cause pain or swelling, it may be a sign of a more serious condition—most commonly varicose veins or chronic venous insufficiency. These conditions occur when the valves inside the veins weaken or become damaged, allowing blood to pool and causing the veins to twist, stretch, and enlarge. This is most often seen in the legs, where gravity makes it harder for blood to return to the heart.
Several risk factors contribute to the development of varicose veins, including:
Family history (genetics)
Prolonged standing or sitting
Obesity
Smoking
Hormonal changes, especially during pregnancy or menopause
A sedentary lifestyle
While many cases are mild and can be managed at home, some situations require medical evaluation. Seek professional care if you notice:
Persistent or worsening pain
Heaviness or aching in the legs
Skin discoloration around the veins
Open sores (venous ulcers) near the ankles
Hard or warm veins, which could suggest a blood clot
Treatment for bulging or varicose veins depends on the severity of symptoms. Common conservative options include:
Wearing compression stockings to improve circulation
Elevating the legs when resting
Regular low-impact exercise, such as walking or swimming
Weight loss, if applicable
Avoiding long periods of standing or sitting
In more advanced cases, a healthcare provider may recommend procedures like:
Sclerotherapy (injection of a solution that closes the vein)
Laser therapy
Vein stripping or ligation (surgical removal of the vein)
Endovenous ablation, which uses heat to seal the affected vein
If left untreated, advanced venous disease can lead to serious complications, including venous ulcers, skin infections, and a higher risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT)—a dangerous condition where blood clots form in deep veins, potentially leading to life-threatening events like a pulmonary embolism.
Preventive steps can significantly reduce the risk of developing problematic veins. These include:
Maintaining a healthy weight
Engaging in daily movement or exercise
Wearing loose, non-restrictive clothing
Elevating your legs periodically
Avoiding tobacco products
Staying hydrated and managing blood pressure
In conclusion, while bulging veins are often a cosmetic concern with no serious health risks, they can sometimes signal a deeper problem. Staying aware of your body’s changes and acting early when symptoms arise is the best way to protect your long-term vascular health.